1. Understanding Renting and Leasing
a. Definitions
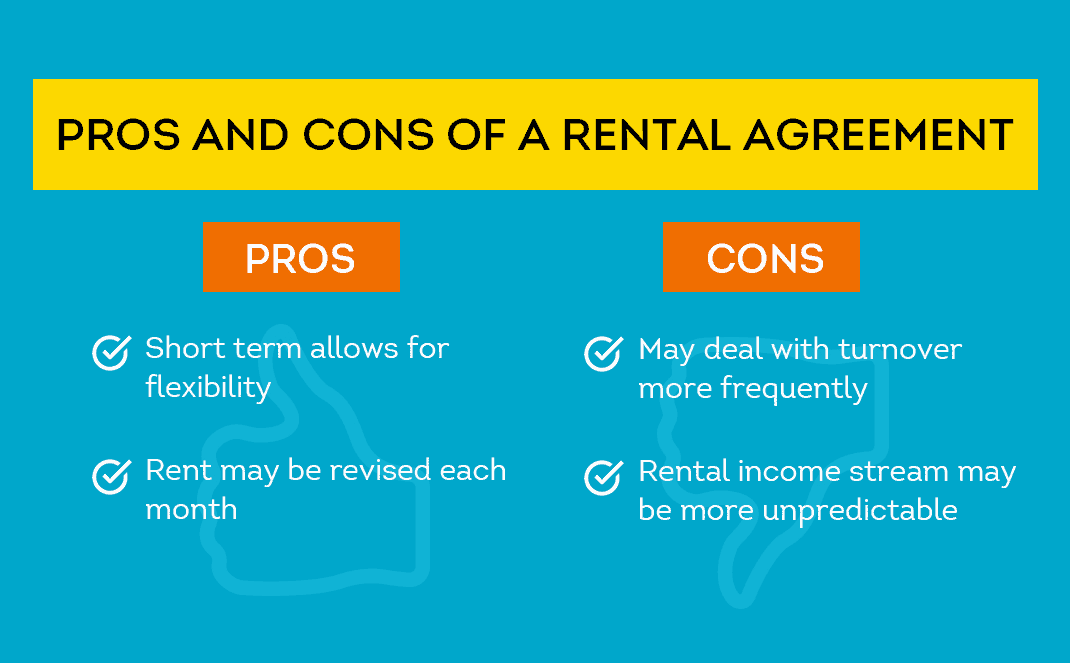
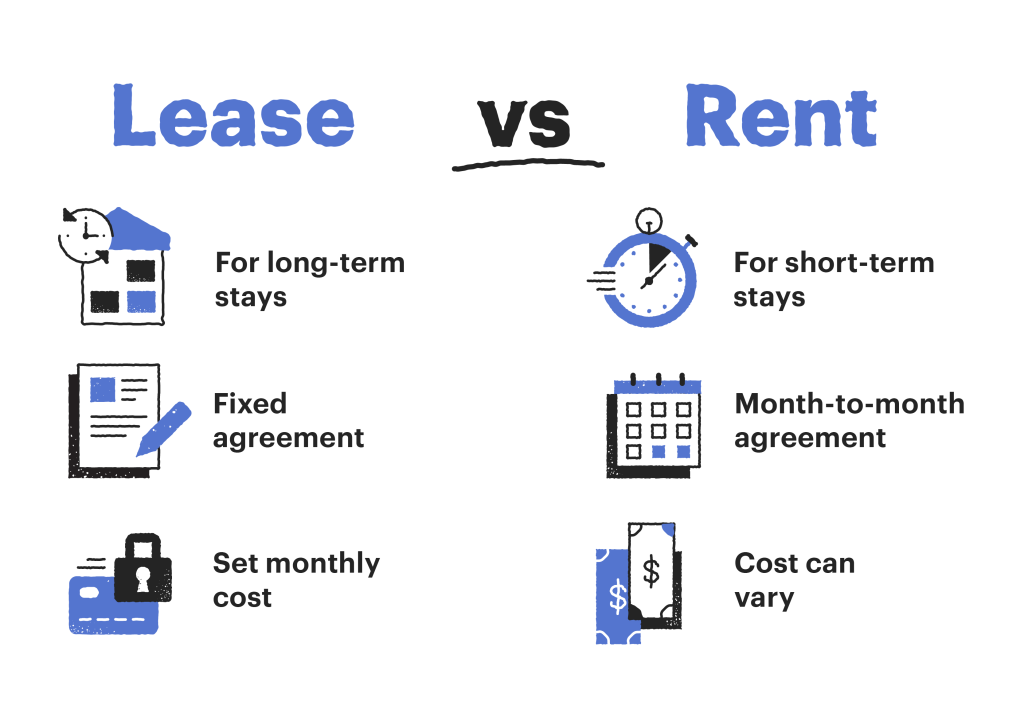
Renting: Renting is a short-term agreement where a tenant pays the property owner (landlord) to occupy a property for a specified period, typically on a month-to-month basis. The terms of renting are often more flexible, allowing either party to terminate the agreement with proper notice.
Leasing: Leasing involves a longer-term agreement where a tenant signs a lease contract to occupy a property for a fixed period, usually six months to several years. Lease agreements provide more stability but are less flexible than rental agreements.
2. Benefits of Renting
a. Flexibility
- Short-Term Commitment: Renting offers the advantage of short-term commitment, making it ideal for individuals who may need to relocate frequently or are uncertain about their long-term plans.
- Ease of Termination: Rental agreements can often be terminated with relatively short notice, providing flexibility for tenants.
b. Lower Initial Costs
- No Large Down Payment: Renting typically requires a security deposit and the first month’s rent, which is significantly less than the down payment required for purchasing a property.
- Maintenance Costs: In most rental agreements, the landlord is responsible for property maintenance and repairs, reducing the financial burden on tenants.
c. Access to Amenities
- Included Amenities: Many rental properties come with included amenities such as gyms, pools, and laundry facilities, which may be costly to install or maintain in owned properties.
- Location: Renting can provide access to desirable locations that may be unaffordable to purchase in, such as urban centers or upscale neighborhoods.
3. Benefits of Leasing
a. Stability and Predictability
- Fixed Terms: Lease agreements offer stability with fixed terms and rental rates, providing predictability for tenants and landlords alike.
- Protection from Rent Increases: Lease agreements typically lock in the rental rate for the duration of the lease term, protecting tenants from sudden rent increases.
b. Customization
- Personalization: Tenants may have the option to customize the property to their liking, such as painting walls or making minor renovations, with the landlord’s permission.
- Long-Term Planning: Leasing provides a stable environment for long-term planning, whether for residential living or business operations.
c. Investment Security for Landlords
- Guaranteed Income: Landlords benefit from a guaranteed rental income for the duration of the lease, reducing the risk of vacancy and ensuring steady cash flow.
- Tenant Responsibility: Long-term tenants are often more invested in maintaining the property, reducing wear and tear and the need for frequent repairs.
4. Considerations When Renting or Leasing
a. For Tenants
1. Budget and Affordability:
- Monthly Rent: Ensure the monthly rent fits within your budget, considering other expenses such as utilities, insurance, and maintenance fees.
- Initial Costs: Factor in initial costs such as security deposits, application fees, and moving expenses.
2. Lease Terms:
- Duration: Understand the lease duration and any penalties for early termination.
- Renewal Options: Check if there are options to renew the lease and under what conditions.

3. Property Condition:
- Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection of the property before signing the lease to identify any existing damages or issues.
- Maintenance Responsibilities: Clarify who is responsible for maintenance and repairs, and ensure this is detailed in the lease agreement.
4. Location and Amenities:
- Convenience: Consider the property’s proximity to work, schools, public transportation, and essential services.
- Amenities: Evaluate the availability and quality of amenities included with the property.
5. Legal Rights and Obligations:
- Tenant Rights: Familiarize yourself with local tenant rights and regulations to ensure you are protected in case of disputes.
- Lease Agreement: Read the lease agreement carefully and seek legal advice if necessary to understand your obligations and rights.
b. For Landlords
1. Tenant Screening:
- Background Checks: Conduct thorough background checks, including credit history, rental history, and employment verification, to ensure reliable tenants.
- References: Obtain references from previous landlords to assess the tenant’s reliability and behavior.
2. Lease Agreement:
- Clear Terms: Draft a clear and comprehensive lease agreement outlining rent, payment schedules, maintenance responsibilities, and rules for property use.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure the lease agreement complies with local laws and regulations to avoid legal issues.
3. Property Maintenance:
- Upkeep: Regularly maintain and inspect the property to ensure it remains in good condition and meets safety standards.
- Emergency Repairs: Establish a system for handling emergency repairs promptly to maintain tenant satisfaction and property value.
4. Rent Collection and Financial Management:
- Payment Systems: Implement reliable systems for rent collection and financial management to ensure timely payments and accurate record-keeping.
- Security Deposits: Manage security deposits according to local regulations and return them promptly at the end of the lease term, minus any allowable deductions.
5. Communication and Relationship Management:
- Open Communication: Maintain open and professional communication with tenants to address concerns and resolve issues promptly.
- Tenant Retention: Foster good landlord-tenant relationships to encourage long-term tenancies and reduce turnover rates.
Conclusion
Renting and leasing are vital components of the real estate market, offering flexibility, stability, and a range of options for both tenants and landlords. Understanding the benefits, challenges, and key considerations of each approach can help you make informed decisions, whether you are looking for a place to live, a commercial space for your business, or managing rental properties. By carefully evaluating your needs, conducting thorough research, and adhering to best practices, you can navigate the renting and leasing process successfully and achieve your real estate goals.
4o











